Introduction to Cybersecurity in Networks and Systems
Motivation for Cybersecurity
- Computers have become part of our daily life
- We are progressively becoming more and more dependent on these tools, and many times we store and share sensitive information with others through the Internet
- Because the Internet is a shared space, it cannot be trusted, and special security policies must be enforced by applying the right security mechanisms
CIA (Confidentiality/Integrity/Availability)
Confidentiality:
Definition: Absence of disclosure of data by non-authorized parties
-
Confidentiality ensures that only the right authorized parties have accessed to the information being shared
-
Security Properties:
- Privacy
- Segregation of privileges
Integrity:
Definition: Absence of invalid data or system modifications by non-authorized parties
-
Integrity ensures that the data being secured can only be altered by the authorized parties
-
Security Properties:
- Authenticity - Integrity of content and origin
- Non-repudiation - author of information cannot deny authorship
Availability:
Definition: Readiness of system to provide service
- Availability ensures that a certain system that provides a service to its clients is down the least time possible
Definitions
Vulnerability: characteristic of a system that makes it susceptible to an attack
Attack: actions that lead to a violation of a security attribute
Threat: Attack that may potentially happen; for this, we need a vulnerability, an actor and a motive (someone with a reason to attack the system)
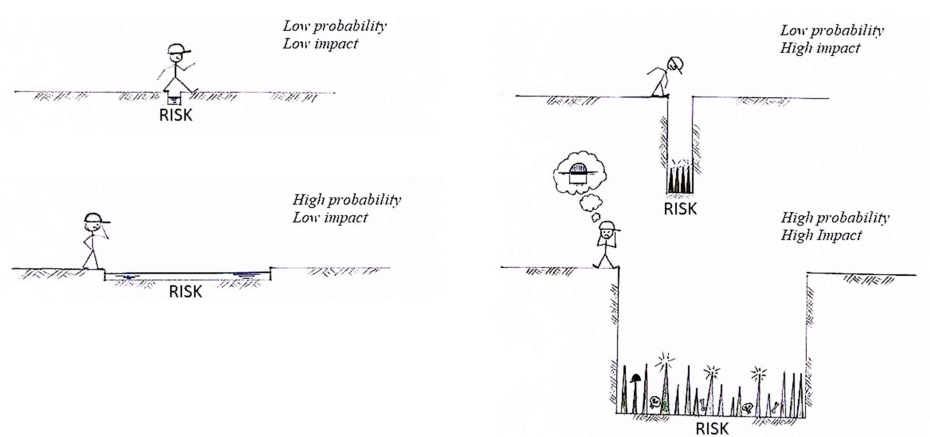
Our mission
- The mission of cybersecurity specialists is to create security policies and security mechanisms to reduce the risk
Risk: Combines two parameters: The probability that something bad will happen with the damage that it will cause if it does happen
Security Policy: A security policy defines, in a shared space and for a given piece of information, who should have access to this information, and who shouldn't, establishing constraints that should be respected
Security Mechanism: A security mechanism is the tool/procedure that is used to enforce a certain security policy
Example:
- Security Policy: All data sent to clients should not be disclosed by potential attackers spoofing the network
- Security Mechanism: Using TLS/SSL to encrypt the communication with the clients